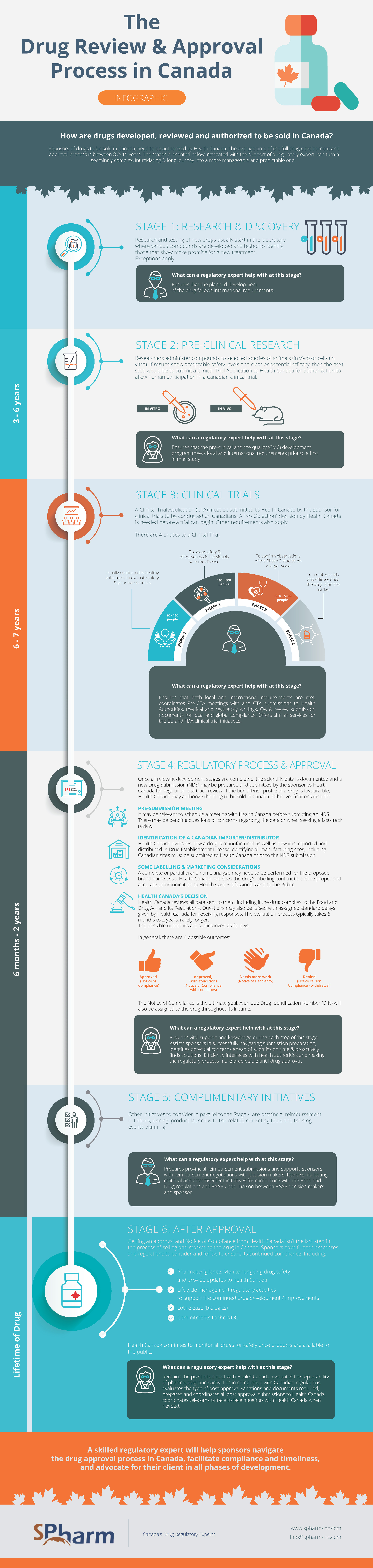
How are drugs reviewed and authorized for sale?
Most health products, including drugs to be marketed or sold in Canada are reviewed and authorized by the Health Products and Food Branch (HPFB) of Health Canada, more precisely, under the Therapeutic Product Directorate (TPD) or the Biologic and Genetic Therapies Directorate (BGTD), for drugs and biologic, respectively. Each of these Directorates have specific offices and bureaus. Drugs are authorized to reach that market only once they have successfully gone through the relevant Bureau review process, responsible for assessing their safety, efficacy and quality, and, received a favorable decision. Even after a health product receives a favorable decision and can proceed with its sale in Canada, monitoring of its effectiveness and safety continues.
What is Canada’s Health Products and Food Branch?
Health Canada’s HPFB is the national authority that is responsible for regulating, evaluating, and monitoring the safety, efficacy, and quality of drugs, biologics, genetic therapies and other health products available for the Canadian marketplace. The HPFB’s mandate is to manage the health-related risks and benefits of health products and foods for Canadians.
THE DRUG DEVELOPMENT PROCESS
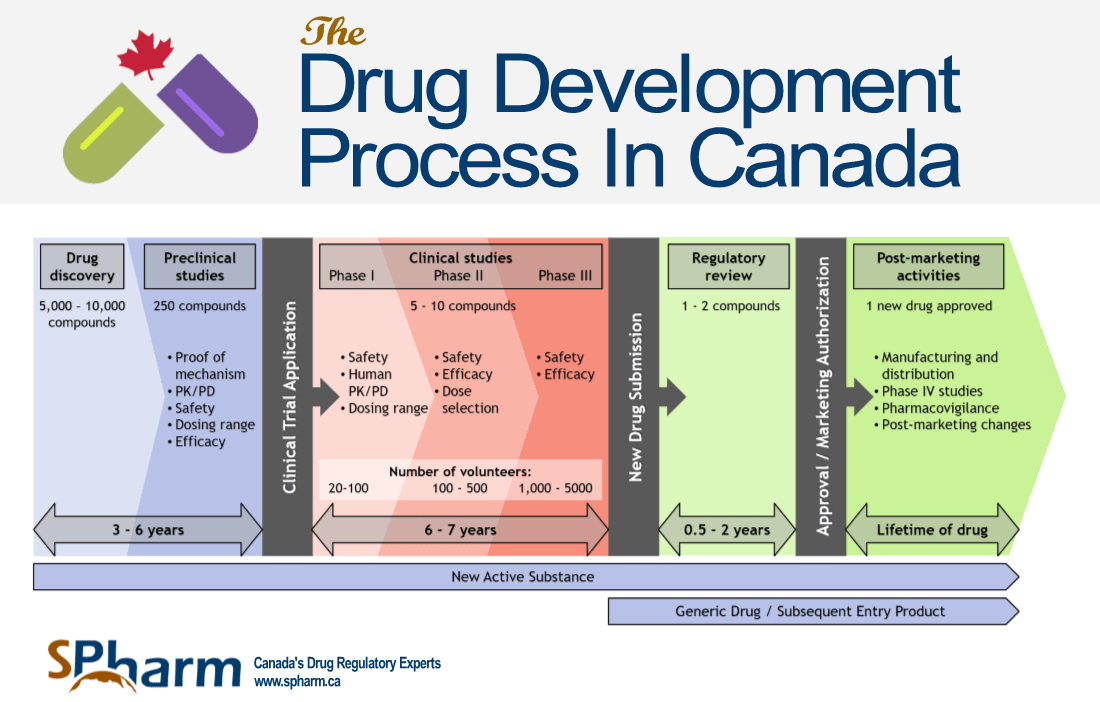
We have categorized the drug development process in 5 stages and have provided a graphic below to accompany the text.
STAGE 1: INITIAL DRUG RESEARCH
Researchers start by discovering and identifying various chemical, biological substances or other products on the way towards developing a drug. This can be done through new information regarding a disease process, many tests of molecular compounds to find possible beneficial effects, existing treatment that have unanticipated effect and new technologies. Once the researchers have identified a promising compound, they perform testing for activity, efficacy, toxicity and ultimately, gather preliminary information on its effectiveness and safety. This initial research can take a few years of experimentation. If the results are promising, researchers will proceed to the next step of development.
A representation of the Drug Development Process is presented in the graphic below:
STAGE 2: PRE-CLINICAL STUDIES
The next step in development is where researchers administer the drug to selected species of animals (in vivo) or cells (in vitro). The drug must be shown to cause no serious harm (toxicity) at the doses required to have an effect. If results from these initial studies are promising and further tests show acceptable safety levels and clear or potential efficacy, then the next step would be to submit a Clinical Trial Application to the TPD or BGTD for authorization to allow human participation in a Canadian clinical trial.
STAGE 3: CLINICAL TRIALS
All drugs authorized to be marketed or sold in Canada must have been studied in clinical trials. The information gathered from these trials are then included in the relevant regulatory dossiers to be reviewed for the drug to be eventually authorized for sale in Canada by the HPFB, through its relevant Directorate. The results of clinical trials conducted in humans are key components of the review process by the HPFB. The purpose of a trial is to gather clinical information about a drug’s effectiveness, safety, determine best dosing/usage in humans, evaluate any adverse drug reactions and compare results to already existing treatments for the same disease or condition or, to placebo when no treatment already exists for the aimed pathology (when ethically possible).
Clinical Development:
If clinical trials have already been done in Canada and/or in other countries, that is, at the end of the clinical development plan, the sponsor may choose to file a New Drug Submission with the HPFB in order to gain authorization to market and sell the drug in Canada (see New Drug Submission process section below).
However, when a sponsor aims to conduct a clinical trial in Canada, during the clinical development program, then a Clinical Trial Application (CTA) must be submitted to be reviewed and approved by the HPFB’s relevant Directorate in order to proceed with the trial. The results of these studies will be part of the drug approval process.
Clinical Trial Applications:
The Canadian CTA dossier consists of the following documents (exceptions are possible): administrative form, protocol, protocol summary (Health Canada’s template), Informed Consent Form, Investigator’s Brochure and quality dossier summary (Health Canada’s template per study phase).
Health Canada reviews the CTA and notifies the sponsor within 30 calendar days from the date that the application is considered complete. Questions may be issued during the review, and the sponsor will have 2 calendar days to provide the response (exceptions can apply). Note that CTAs are required for phases I to III clinical trials. The authorization (No Objection Letter) is mandatory prior to initiating the trial and importing the investigational product(s) in Canada.
If the HPFB provides authorization, the study can be underway with human subjects that are informed and have given their consent to be administered the drug for their participation. Note that a Canadian Ethic Committee must also approve the study material (protocol, Investigator’s Brochure and Informed Consent Form). Tests are conducted in a controlled environment where drug administration procedures and results are closely tracked, monitored and analyzed.
Clinical Trial Phases
There are, in summary, four (4) phases in the clinical trials process. Each clinical trial phase for drugs has a different purpose.
Phase 1 – The Safety phase
This phase usually tests an investigational drug on a small group of healthy individuals for the first time (except when not ethically acceptable to do so). The purpose is to determine the pharmacokinetics/pharmacological action of the drugs, find a safe dosage range and identify adverse drug reactions.
Phase 2 – The Effectiveness phase
In this phase, the drug is given to a larger group of individuals with the pathology to be treated (usually several hundred). The purpose is to obtain data on the effectiveness of the drug, to further assess the drug’s safety and to determine the best dose.
Phase 3 – The Confirmation Phase
If the results from Phase 2 look promising, the drug manufacturer would proceed into Phase 3 trials. In this phase, the drug is given to even larger groups of patients (usually in the thousands). The purpose of this phase is to confirm the drug’s effectiveness, monitor side effects, compare the drug to other commonly used treatments and to collect further information that will allow the drug to be used and marketed safely.
Phase 4 – The Monitoring phase
Phase 4 trials are done after the drug is already approved and sold on the market. The purpose of this phase is to gather more information on the best ways to use a drug, and the long-term benefits and risks to the population. Unless agreed to with Health Canada, these studies do not need to be submitted under a Clinical Trial Application, when used according to the terms of the market approval.
If the drug is to be used outside the terms of the market approval (that is in a different population, for a different indication, using a different dose, etc.), the study will not be considered a phase IV. Consequently, in these cases, a CTA will need to be submitted to Health Canada in order to obtain a No Objection Letter.
STAGE 4: APPROVAL PROCESS
If results of all the preclinical studies and the clinical trials show that a drug’s potential therapeutic benefit outweighs its risks (side effects, toxicity, etc.), and the chemistry and manufacturing dossier is complete, then the sponsor may decide to file an NDS with the appropriate HPFB Directorate in order to be granted authorization to sell the drug in Canada. A sponsor can submit an NDS whether the clinical trials were done in Canada or in other countries. The NDS must include the results of the quality (Chemistry and manufacturing), preclinical and clinical studies, whether done in Canada or in other countries.
The drug’s efficacy and safety data is evaluated and the Risk/Benefit analysis is performed, before reaching a decision.
The information requested by Health Canada as part of an NDS application must be detailed enough that Health Canada can make an assessment on the safety and effectiveness of the new drug. All submissions must be provided to Health Canada in an electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD) format.
Common Technical Document
The CTD format originates from the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH) initiatives, in their effort to harmonize efficacy, safety and quality (chemistry and manufacturing) requirements globally for the registration of drugs (pharmaceuticals, biologicals, genetic therapies, …) for human use. This initiative includes standard information organization for new drug registration applications. The CTD format is divided into five modules: Module 1 contains region-specific information and Modules 2–5 contain common clinical, nonclinical and quality information with some regional variations.
The CTD format is presented below.
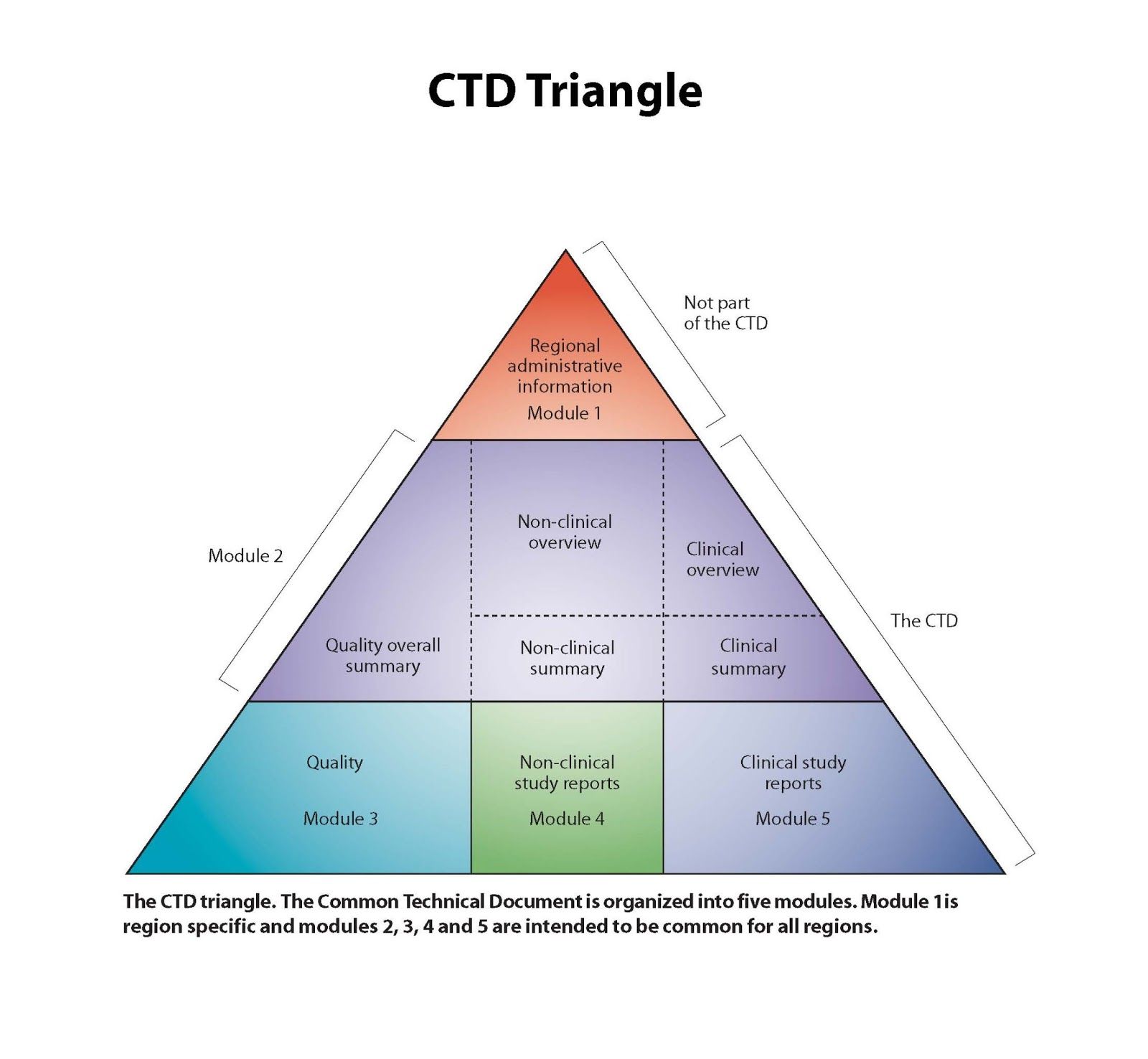
The Module 1 (regional) includes the following, amongst other information:
- Administrative form
- Product Monograph
- Mock-up of Inner and Outer labels
- Certified Product Information Document
- Brand Name Analysis
- Risk Management Plan
- Etc
Abbreviated New Drug Submission
The ANDS regulation was created to make the approval process for generic drugs simpler and more cost effective. Under an ANDS, the manufacturer of a drug has to prove that its product is pharmaceutically equivalent and/and bioequivalent with the innovator’s drug. For the purpose of an ANDS the sponsor may need to perform a bioequivalence study or a physico-chemical comparison (parenteral drugs or drugs for which it is not ethical to conduct the study on healthy volunteer).
Review Process
The HPFB reviews the NDS and all the information about the drug captured during the development process (quality, preclinical and clinical) and evaluates the risks of the drug versus its benefits to the Canadian population. More specifically, HPFB reviews information regarding the drug’s manufacturing, packaging and labelling, as well as, information about the drug’s therapeutic claims and side effects. What Doctors and patients will be told about the drug will also be reviewed, through the drug’s monographs and information sheets. All drugs allowed to be sold in Canada are reviewed to ensure that they meet the requirements of the Food and Drugs Act and its Regulations. Once these requirements are met, the sponsor (usually the Marketing Authorization Holder) would receive a Notice of Compliance, confirming the dossier’s compliance with the Food and Drugs Act and its Regulations.
How long does the review process take?
The target review timeline ranging from 7 months (accelerated review and ANDS) to 1 year (standard NDS). The exact time for Health Canada to review drug safety and efficacy information from an NDS depends on the type of drug, the quality of the dossier, the amount of questions that Health Canada raises during the review process, the answers provided by the sponsor and if the targeted timelines for the responses are respected. Once the review is complete, the Regulatory Agency decides to approve (or reject) the use of a new medication. In some instances, it can take longer than the targeted review timelines. HPFB review timelines are based on internationally competitive performance targets that are usually respected. By experience, the review can take anywhere from 6 months to 2 years, rarely more. The average time of the full drug development and approval process from initial research, preclinical studies, through the 3 phases of clinical trials to drug approval is 12 years (between 8 & 15 years).
NEW DRUG APPROVAL DECISION
Notice of Compliance
Once the review is complete, if the conclusion is that the benefits of the drug outweigh the risks, that the risks can be managed and confirming the dossier’s compliance with the Food and Drugs Act and its Regulations, then the sponsor in Canada receives a Notice of Compliance (NOC), as well as a Drug Identification Number (DIN), which is specific to a drug product to be sold on the Canadian market.
Notice of Non-Compliance
Upon the completion of the review process, if the HPFB finds that there is insufficient evidence to support the safety, efficacy or quality claims of the drug, HPFB will not grant a marketing authorization for that drug. At this point, the sponsor typically has 3 options: to supply additional information to the HPFB, to re-submit a submission at a later date with additional supporting data (without prejudice), or to ask that HPFB to reconsider its decision.
Priority Review or Accelerated Review Process
For health conditions that are serious, life-threatening or for a severely debilitating disease (such as Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, AIDS, or Parkinson’s Disease), the HPFB can provide faster authorization of a drug as follows:
- Priority Review : Applies to drugs that shows substantial evidence of clinical effectiveness at the end of the clinical trial phases.
- Notice of Compliance with conditions : Applies to drugs with promising evidence of clinical effectiveness throughout the clinical trial phases. Approval would be granted to a manufacturer to market and sell that drug in Canada with the condition that the manufacturer execute additional studies to confirm the drug’s benefit and safety.
To be considered for PR or NOC/c, the drug must meet the following standards as described by Health Canada; the drug must provide:
- effective treatment, prevention or diagnosis of a disease or condition for which no drug is presently marketed in Canada; or
- a significant increase in efficacy and/or significant decrease in risk such that the overall benefit/risk profile is improved over existing therapies, preventatives or diagnostic agents for a disease or condition that is not adequately managed by a drug marketed in Canada
Related to the NOC/c, some of the conditions of the Notice of Compliance include a requirement to closely monitor the drug for safety and to provide HPFB with regular updates. Once the conditions are met, the designation of “with condition” is removed from the NOC.
STAGE 5: AFTER APPROVAL
Once a health product is approved and, on the market, the HPFB requires a sponsor to ensure that the use of its drug is done under the terms of its market authorization. In addition, Life Cycle Management activities (post approval submissions to Health Canada, for new indications, new dosage forms, new strengths, manufacturing changes, etc.) are required to ensure the maintenance of the product License with its related improvements. In summary, sponsors need to ensure its continued compliance with the Food and Drug Regulations, while their products are on the market.
On the other hand, Health Canada monitors drug information & adverse drug reactions reporting, conducts market surveillance, investigates complaints and manages recalls if necessary, amongst other things.
There are also more processes and regulations to follow and consider, either before, during or after the review process, and before that drug is officially marketed, distributed and sold in Canada. Topics such as licensing, warehousing, wholesale distribution rules and the Drug Establishment Licence (DEL), regulations around distribution to consumers, regulations around the marketing and advertising activities, provincial requirements, health insurance funding rules, among others.
All of these topics are worthy of their own article and are beyond the scope of this one.
SUMMARY
Health Canada is the federal body that regulates the drug approval process under the Food and Drugs Act (FDA) and its regulations (FDR), its related policies and guidance. Before a drug can be distributed and sold in Canada, its manufacturer must receive a Notice of Compliance (NOC) from Health Canada, and the drug must be assigned a Drug Identification Number (DIN), uniquely identifying all drug products sold in a dosage form in Canada. New drugs must also go through extensive testing before being granted an NOC.
It can take anywhere from 6 months to 2 years for Health Canada to review drug safety and efficacy information before providing a decision on whether an NOC is to be granted. Once granted, it represents that the drug meets the required standards under the Food and Drugs Act and its regulations, for use in humans. The monitoring for drug safety continues even once the drug finally makes it to consumers.
The process of marketing and selling any new drug in Canada can certainly seem complex or intimidating. However, for drug companies seeking approval of their new drug in Canada, a number of strategies are recommended to make the process more effective. Focusing on preparedness, having proper data and documentation from research & trials and following proper guidelines are valuable recommendations to follow.
Another recommendation is for drug companies or sponsors to work in collaboration with Canadian regulatory experts so as to optimize the registration process to ensure the best strategic registration initiatives, to anticipate the health authority’s potential concerns and to help in finding proactive solutions prior to submitting to Health Canada. Working with regulatory experts or consultants can help avoid unwanted review complications and delays and therefore, reduce cost consequences of potential market entry delays.
Following the above recommendations will help turn a seemingly complex or intimidating Drug approval process into a more manageable and predictable one.
INFOGRAPHIC
For an infographic rendering of the above drug review and approval process in Canada, please click on the image below to have the option of downloading it in either PDF or JPEG version.
For further information about the drug review & approval process in Canada, please contact Spharm directly.